Restorative dentistry
PREVENTION OF AND THERAPY FOR TOOTH DECAY
#zubnykazdc
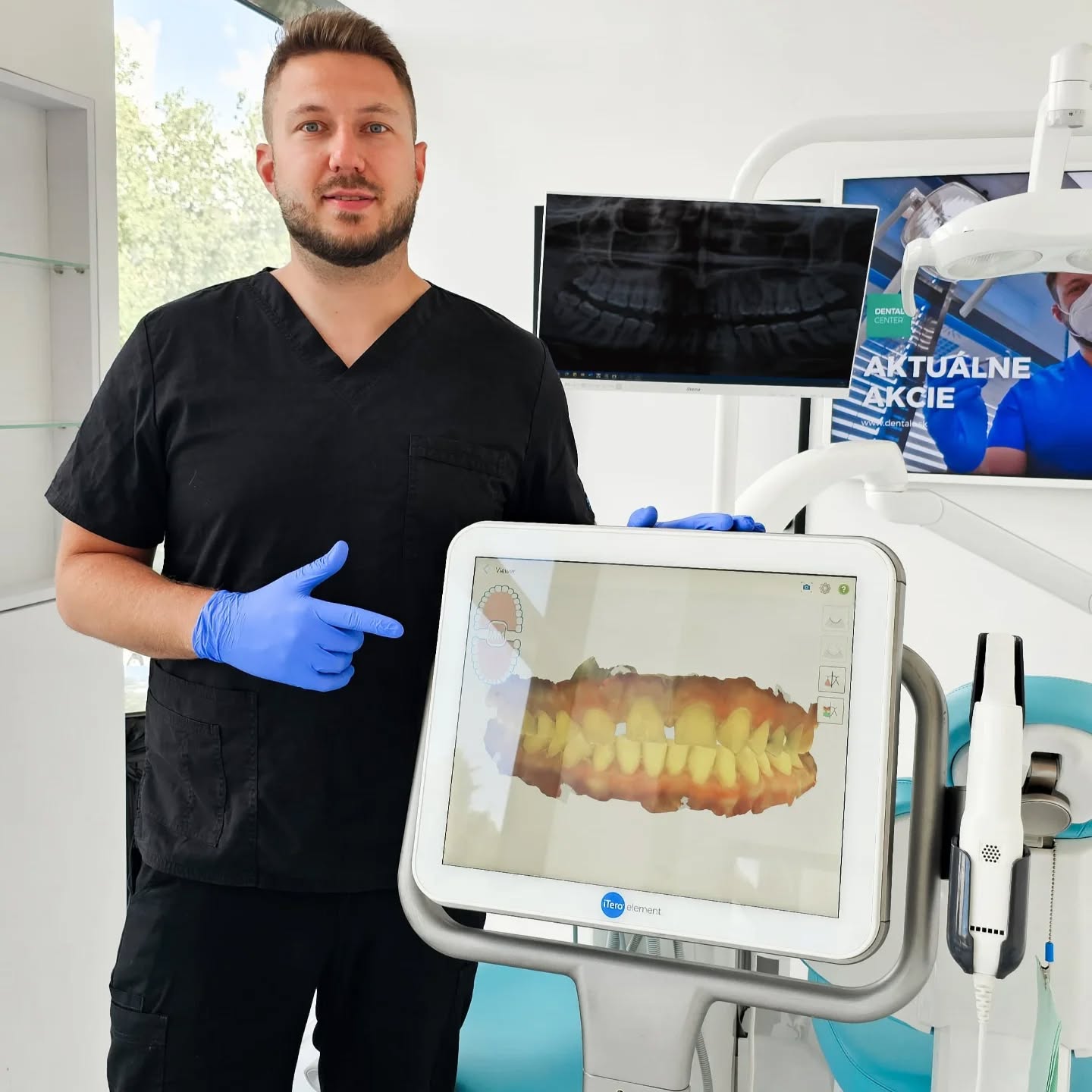
The main aim of restorative dentistry is to save an affected tooth. Restorative dentistry is the basic discipline of dentistry, as its focus is the prevention and treatment of dental caries and its consequences, i.e. inflammation of the dental pulp, inflammation of the periodontium and the periosteum and dental focal infections. Restorative dentistry is a branch of dentistry that deals with the repairing of defects in teeth, such as with fillings or by performing root canals.
The primary aim of restorative dentistry is to save an affected tooth. For cases of minor damage that do not affect the nerves of the tooth, these defects can be resolved with a filling. The type of filling itself, whether white or amalgam, is determined individually according to the assessment of all current circumstances and the wishes of the patient. If the tooth has more serious damage, treatment of the root canals – endodontics – is done.
Tooth decay
Tooth decay is one of the most widespread infectious diseases, affecting nearly the entire population and doing so from an early age. One of the main reasons is our diet, which contains large amounts of sugars, which create the right conditions in the oral cavity for the proliferation of microorganisms.
With tooth decay, the hard dental tissues are damaged, meaning their disruption, disintegration and loss occur. Three factors have to be present for the development of dental caries:
-
Sensitive tooth surface
-
Cariogenic food (sugars)
-
Microorganisms
Therapy
-
Amalgam and photocomposite fillings
-
Preventive fillings
-
Fibreglass fillings
Length of treatment
In restorative dentistry the period of treatment depends on the range of the work to be done.
Who it is intended for/period of repeating
Restorative dentistry is intended for all patients who have certain tooth defects.
Why this treatment?
- quick access to an appointment
- qualified personnel
- expertise
- pain-free
- modern equipment
- quality of the materials
* You can register at klient.dcmedical.eu and use credit payment, where with the highest bonus you pay the highest price | Anyone can register, even a new client/patient
** Prices are orientational only | The final price depends on the complexity and range of the interventions, which we will confirm upon consultation | The price list is valid on date 13.7.2025